Credit Suisse is one of the biggest banks in the world. It is so huge that it generated a revenue of 22 billion dollars, operates in over 50 countries, and its assets under management alone amount to 1.1 trillion dollars. But in the past year, something crazy happened. They lost more than 14 billion dollars in two terrible Investments, have reported five quarters of loss in the past seven quarters, and have laid off 5000 employees.
This combined with the pandemic, the Russia-Ukraine war, and UK’s economic turmoil. All of them have put this giant Bank at a big risk. This situation is so critical that experts fear that it could lead to another nightmare like the 2008 recession as a result just like Lehman Brothers in 2008. Its stock price fell by 60% in 2022.
If this Theory comes true and Credit Suisse goes bankrupt just like in 2008. It’s going to cause one of the worst recessions of the 21st century.
What exactly is wrong with Credit Suisse?
To understand the Credit Suisse problem we first have to understand something called CDS or credit default swap. These words might sound very complex and very intimidating but don’t worry about it at all I will explain it in such a way that even a 15-year-old will be able to understand this.
Just stay with me and read this very carefully
How Does Bonds Work
As we learned just like govt. issues bonds there are even private companies that give out bonds. So let’s say Adani ports need capital of one million dollars or 10 lakh dollars. Because they have such an amazing brand value they will float a bond and borrow money from common people like you and me.
But one person cannot give Adani one million dollars right so what would Adani do? They will break this one million dollar Bond into ten thousand Euros. Whereby each unit will be worth a hundred dollars and over a five-year period the adonis will pay back the investors a three percent interest. So when 10,000 people buy these hundred dollar units they’re essentially lending the Adani’s hundred dollars each and one million dollars collectively.
Suppose, one of these investors is “Nitya” who bought one unit of this bond for 100 dollars. So firstly Adani would pay Nitya’s other investors three dollars at the end of every year. Then after five years, they would return the principal amount of 100 dollars. This is how a bond works.
What is CDS or Credit Default Swap (Explanation with Example)
Let’s say tomorrow there is news that UK and US both could experience a recession because of this panic in the market. Nitya is scared that Adani won’t be able to pay back her 100 dollars similarly even other investors are scared.
So this is where an insurance company comes in which tells Nitya that they will ensure this bond for her if she just pays a two percent fee of the bond unit. So if Nitya pays two dollars to this insurance company tomorrow if the Adani are not able to pay back 100 dollars to Nitya then the insurance company will pay Nitya 100 dollars.
This is what you call a credit default swap. Whereby an insurance company takes the risk on behalf of the investor whois Nitya. If the borrower defaults in this case if Adani defaults now the question we hear is what is the benefit for the insurance company over here because after all Nitya is just paying two dollars and she’s getting 100 dollars in case of default.
How insurance companies make profit with CDS?
Just like Nitya there will be 15,000 investors who will buy two-dollar insurance to ensure their 100-dollar units. If 15,000 people buy the insurance then the insurance company will have thirty thousand dollars in its account. Out of these fifteen thousand borrowers, the probability is that only 100 of them will lose their money. So the insurance company only has to pay 100 dollars to these 100 people as in just ten thousand dollars. which means they will still make a profit of twenty thousand dollars. So just like our normal Insurance even here the insurance company depends on probability to make profits. By the way, this insurance company could be any entity. It could be an insurance company, a bank, or even a hedge fund.
If this is clear to you let’s try to understand
How did this Credit Default Swap Indicate the 2008 Crisis
So let’s take you back to 2008 America. This is when there were a lot of people who are needing home loans and there were a lot of banks who were willing to lend money. So let’s say there are five home buyers wanting a loan of two hundred thousand dollars each. So the bank would lend a total of 1 million dollars to these five home buyers at six percent interest. Now in addition to that what the bank would do is instead of giving out their own money the bank will get one million dollars from a rich investor named “Riva”. Then they would distribute his 1 million dollars into five parts as loans to home buyers and in return, they would agree to give Riva 3% interest.
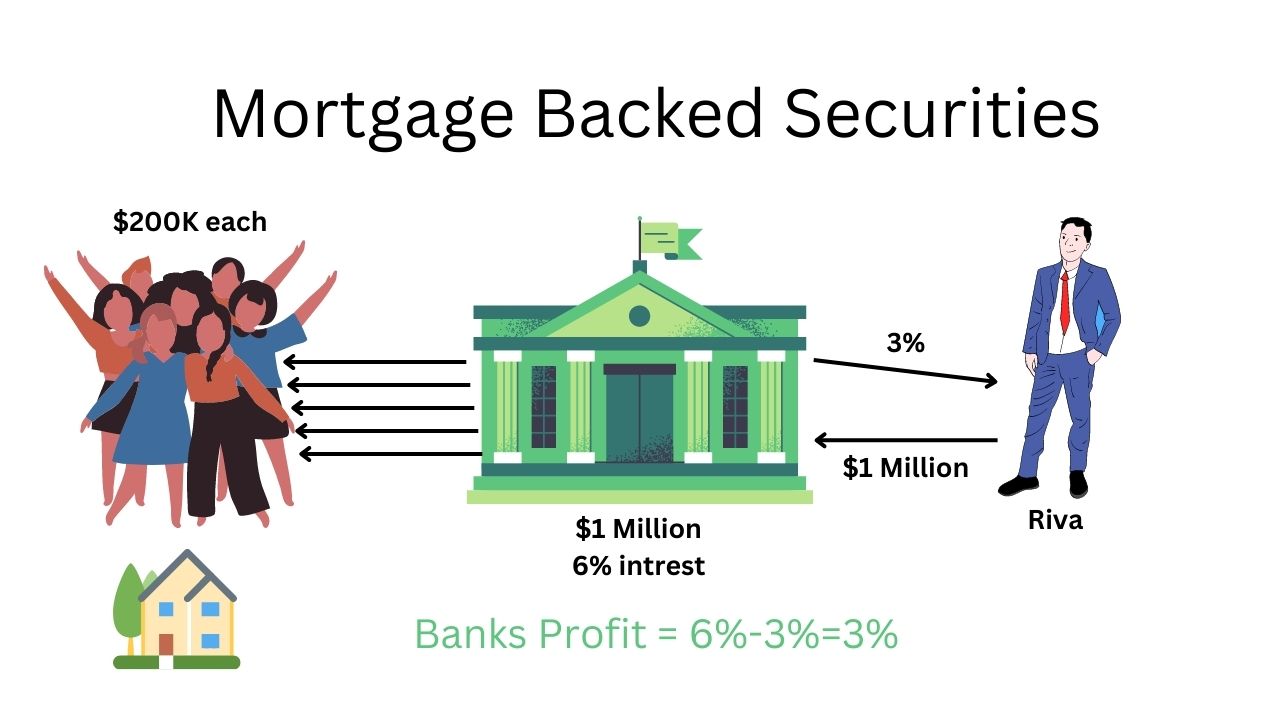
So you see what happened the bank is charging a six percent interest to the home buyers but is giving a three percent interest to Riva. Therefore the remaining three percent will be the bank’s profit. This is what you call as mortgage bagged securities. Whereby the bank takes a group of loans and sells them to an investor such that the investors get returns and the banks get profit without investing their own capital. So now Riva is happy that the bank is taking the risk of finding credit-worthy borrowers, the borrowers are happy because the bank is quickly dispersing loans, and the bank is happy because without using their own Capital they are still able to make a profit with 3% interest.
Now pay attention to this. As more and more loans got disbursed the bank Executives got scared so just like Nitya went to an insurance company even these Banks go to an insurance company. And just like Nitya got a 100-dollar Bond unit insured for two dollars, these banks will pay a one percent fee to get their one million dollar loan units. So they would pay 10,000 dollars as insurance for a one million dollar loan unit or one million dollars worth of mortgage-backed security.
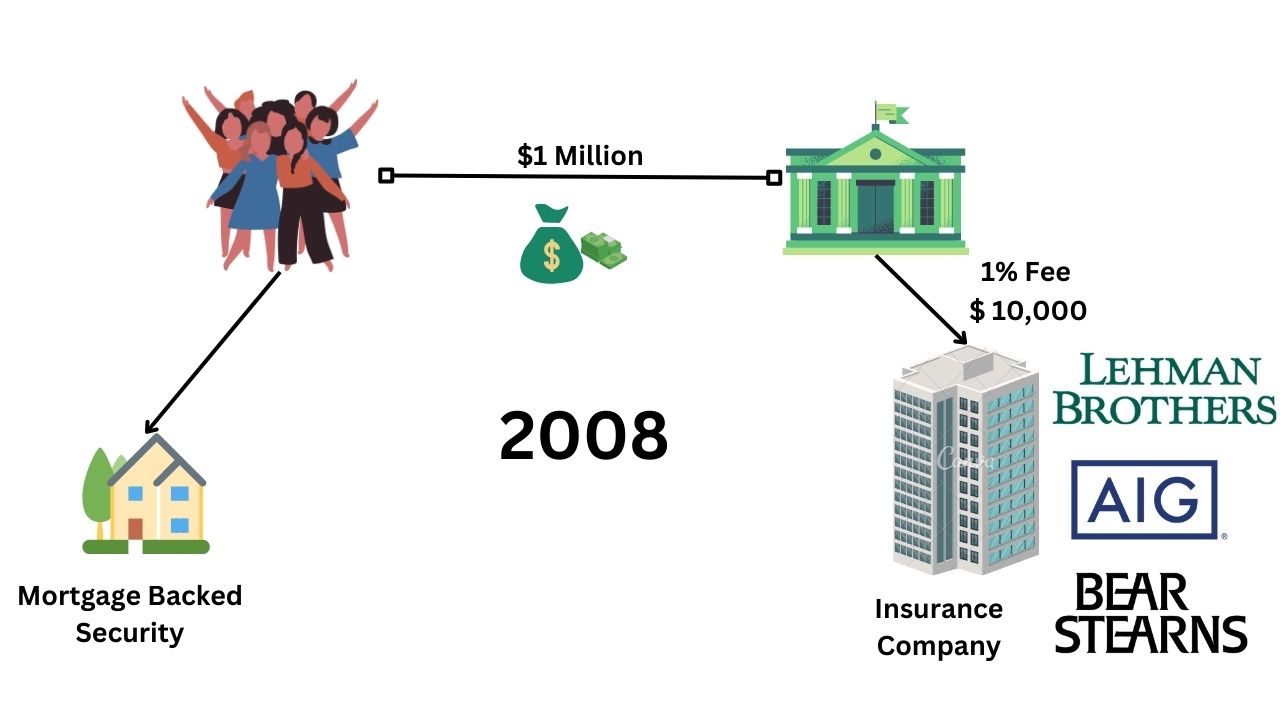
So tomorrow if these home buyers are not able to pay back these loans the insurance company will have to pay the bank 1 million dollars. This is what happened in 2008 and these insurance companies were none other than companies like “American International Group”, “Bear Stearns”, and the infamous “Lehman Brothers”.
You see in this model even though the bank dispersed one million dollars it’s taking no risk at all because they have its loans insured. This is why the problem began. Since these Banks were able to get their loans insured for just one percent of the amount, they became extremely careless and kept on giving loans to every Tom Dick, and Harry. In fact, after a certain point, these Banks were giving out loans so easily that in 2007 a 22-year-old stripper was able to get a 2.4 million dollar loan and bought 10 houses in just 90 days.
This is where something crazy happened. Soon enough when too many homes got into the market there were more houses in the market than needed and within some time the cost started to go down, rents went down, and people started defaulting on the loans. When this happened the bank started facing a cash crunch. So what did the banks do they went to the insurance companies to get paid for the defaulted loans. But this is where there was an even bigger problem as it turns out the insurance companies insured so much money that they themselves went bankrupt.
As in if 200 Banks got one million dollars worth of loans insured by paying a one percent fee how much did the insurance company get in Revenue? They got 10,000 dollars from each bank and a total of 2 million dollars. So they practically insured 200 million dollars worth of loans but had only two million dollars as Revenue. This means with this money that they had they could only reimburse two banks for their 1 million dollars of default. And they didn’t have any money to pay the rest 198 Banks whose customers did not pay back the loans. so in short the probability got messed up. Now that the insurance companies didn’t have any money they had to start selling their own assets and start paying the banks, and if they could not they went bankrupt.
This is exactly what happened to “Lehman Brothers”. They gave out so much Insurance to Banks and investors that they had accumulated 85 billion dollars worth of portfolio. Which was four times the value of its shareholder’s equity. Since they could not pay back even after selling all the assets they went bankrupt.
Chain Reaction Due to Lehman Brother Bankruptcy
This is where ladies and gentlemen The Chain Reaction started. When Lehman Brothers went bankrupt most of these Banks could not recover their money they lost billions of dollars, the rich investors like Riva did not get their money back. Some banks and investors even went bankrupt and this is what led to a spiral effect. Whereby the real estate companies could not get loans since nobody was buying houses. The construction companies could not pay their loans and since these projects were unsold these construction companies could not pay for their supplies. And those suppliers could not pay their suppliers, who could not pay their Bank installments. Eventually, people lost jobs, companies went bankrupt, and all of this snowballed into a catastrophe, that caused one of the worst economic crises in human history wiping out two trillion dollars of investor wealth from the stock market.
This is how the 2008 recession happened now the question over here is why am I telling the Lehman Brothers story? and how is this connected to Credit Suisse?
Why are the investors comparing this and the 2008 Lehman Brother crisis?
well that is because one of the most important metrics that indicated this danger was the percentage fee that the Lehman Brothers were charging for the insurance. So when they were charging Nitya two dollars to ensure a hundred dollars worth of bonds the percentage fee was two percent and this is what you call the credit default swap spread or CDS spread The more this percentage the more is the risk of ensuring the credit and this is measured in basis points with 100 base points making up one percent. So if I say the CDS spread is 200 basis points it means the cost of insuring is two percent.
If you look at the Lehman Brothers CDS spread you will see that after a certain point spiked and touched 250 basis points as in 2.5% in March 2008. And immediately after that, we saw the U.S economic collapse, and the scariest fact is that now the CDS spread of Credit Suisse stood at 278 basis points as of 2.78%. This means that just like home buyers in 2008 several businesses and investors have taken loans from Banks and have bought bonds, and these loans and bond units have been credit default swaps as insured by credit sues. When this CDS spread is seen going up it says that the risk of insurance has increased by a large extent. Just like the Lehman Brothers shares fell down to Rock Bottom with its increasing CDS spread.
Credit Suisse has lost about 60% of its market cap this year alone. Although this comparison is too dramatic what we cannot ignore is that the Russia-Ukraine war has shattered the market. Energy prices in the UK have already shot up by 175%, and the pound is depreciated by 21.4%, and the business in UK and Europe is already shrinking. So by the end of 2022 if the businesses who took loans from these Banks start defaulting these banks will have to go to the insurers who in this case will be credit Suisse and other big Banks. If they are not able to pay them back it will again lead to a disaster just like the 2008 crisis.
why is this credit default swap so high specifically for Credit Suisse
Well that is because apart from the pandemic, apart from the Russia-Ukraine related risks, apart from the currency fall. The bank already lost 9.3 billion dollars and 5.5 billion dollars by funding two companies called Green cell and archives that went bankrupt. As a result out of the last seven quarters, they have been profitable only twice.
This is the reason why experts are comparing the Lehman Brothers with Credit Suisse. Because both were considered to be too big to fail, both of them lent money to the borrowers, both in short dangerous amounts of assets, and while Lehman did not see a war Credit Suisse got caught between war and energy crisis, a currency crisis, and even a pandemic. So does this mean Credit Suisse is heading for a crisis and a 2008-type situation is going to happen?
Well like I said even the smartest people on the planet cannot predict a recession. This is why as much as it is important to compare the past to the present and to keep a tab on the market it’s equally important to understand the nuances of the market.
The study materials to help you understand this critical movement in financial history.
It explains the concept of something called the tier one Capital ratio read through it and you will understand Why Credit Suisse is still in a comfortable position as compared to the Lehman Brothers